Hardness Test
General
Hardness testing may be used to determine the hardness gradient across a weld zone and parent material for comparison purposes. The maximum hardness of the weld zone may also be ascertained.
The hardness of a weld and HAZ will give an indication of the weldability of the material and may be used to determine whether the welding procedures are correct or being correctly applied.
Two commonly encountered hardness tests carried out on welds are the Brinell and Vickers hardness tests.
There are other hardness methods used including Rockwell, Rockwell Superficial, through indenter Vickers, ultrasonic contact impedance, knoop and shore.
Vickers pyramid hardness test
BS EN ISO 6507 – Method for Vickers hardness test
This test uses a small pyramid shaped diamond indentor with an angle of 136° between the opposite faces. A force is applied to press the indentor into the surface for a period of 10–15 s. The force applied is variable from 1 to 120 kg (9.8–1176 N); the actual value to use would be obtained from the application specification.
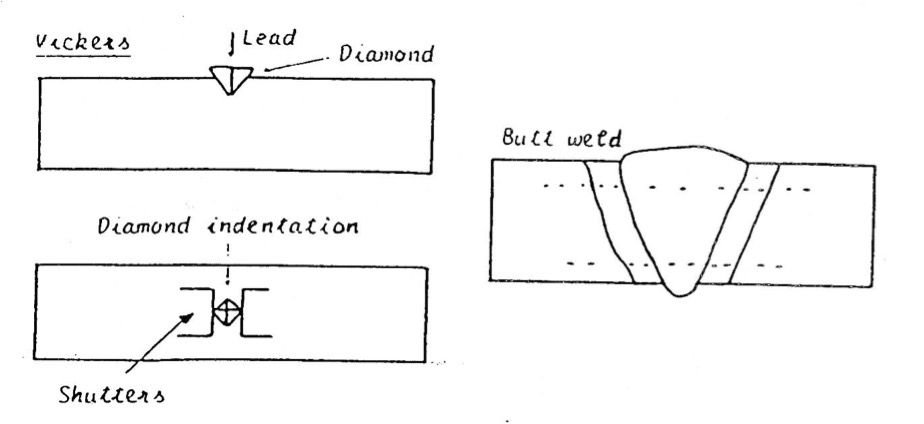
The diamond indentor leaves a pin tip sized square indentation on the surface of the test specimen which is measured by way of a built-in microscope. The diagonal dimension of the indentation is measured using two adjustable shutters; these are integrated with a digital readout, or similar, to give a value which corresponds to indentation depth and therefore hardness.
Hv = Hardness Vickers
However, this displayed value is not the final hardness value. Firstly, both the diagonal lengths need to be measured and averaged. Secondly, the average value needs to be converted to a Vickers pyramid hardness value (Hv) by reference to special tables, or a formula, which also takes into account the applied load. The final hardness value reported should include the load applied, e.g. 200 Hv at 10 kg.
Brinell hardness test
BS EN ISO 6506 – Method for Brinell hardness test
This test is carried out by hydraulically forcing a tungsten carbide ball, 10 mm in diameter, into the surface under test. The force used is 500, 1500 or 3000 kg and is held for 15 s on steel.
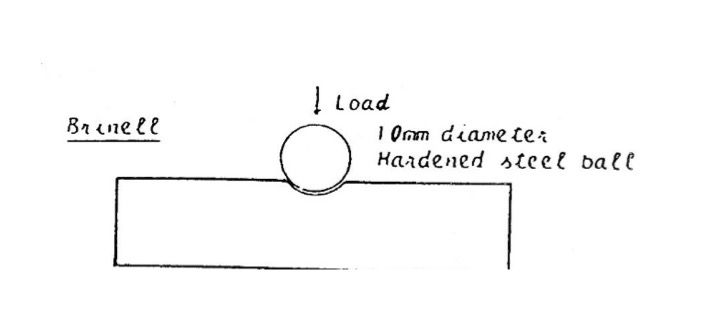
A microscope with a calibrated lens is used to measure the width of indentation, this dimension can then be used with a reference chart or appropriate formula to obtain a Brinell hardness number.